Importance of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology in Dentistry
- July 1, 2021
- Dental Teleradiology
Oral and maxillofacial radiology is a salient part of dentistry that is needed for the diagnosis of oral diseases. An oral and maxillofacial radiologist is specially trained for taking radiographs and interpreting them appropriately for the diagnosis of oral and maxillofacial diseases.
Forms of radiography used in dentistry
- Plain films- intraoral and extra-oral
- Digital imaging
- Advanced techniques – computed tomography, cone beam computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, ultrasound, and nuclear medicine.
Plain Films
They are primarily used to give additional information about teeth and supporting structures after the clinical assessment. Intraoral radiographs (IOPA and bitewings) are good enough to reveal caries, periodontal and periapical diseases, whereas the other conditions involving jaws and temporomandibular joint, can be assessed using extra-oral radiographs.
Digital Imaging
Three types of digital radiography systems used are CCD-charge-coupled device (direct system), CMOS-complementary metal oxide semiconductor (direct system), and PSP-photo-stimulable phosphor (indirect system). When compared with conventional plain film radiography digital radiography has a lesser radiation dose (80%).
Computed Tomography (CT)
It is mostly used for the imaging of complex facial fractures like frontal sinus, naso-ethmoidal region, and orbits. CT can be used to locate the site of fractures before surgical reduction and fixation, especially the undisplaced fractures which are not appreciated well on 2D imaging. CT provides better localization of impacted teeth and its relation to adjacent anatomic structures which is very helpful during surgical removal of impacted teeth.
Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT)
The radiation dose of CBCT is much lesser than that of a conventional CT scan. It has a very high resolution and lesser artifact compared to CT. CBCT can be used for detecting a variety of pathologies, developmental anomalies, traumatic injuries precisely, and for implant planning.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
It is used for imaging the soft-tissue lesions in salivary glands, TMJ and tumor staging. It is ideal for the detection of internal derangement of TMJ.
Ultrasound (US)
It is an important diagnostic tool for cases where MRI is contraindicated. It can be used for detecting pathologies of salivary glands and TMJ. It is a non-ionizing form of radiation so it is much less harmful.
Nuclear Medicine
Nuclear medicine is emerging as a useful imaging modality for diagnosing various oral and maxillofacial diseases including inflammatory lesions to carcinomas. Majorly used for staging and detecting metastasis of carcinomas.
Importance of Oral and Maxillofacaial Radiology
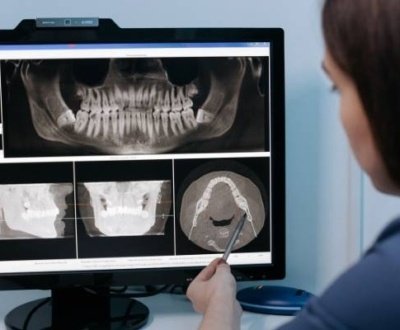
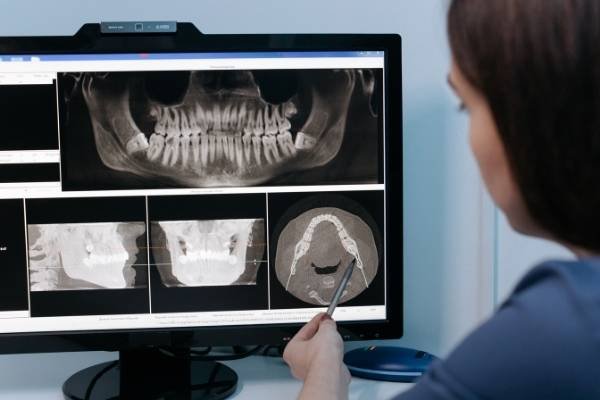
From diagnosis to treatment plan each step in dentistry calls for a supportive radiograph, which can reveal the actual underlying condition of oral tissue and can be correlated with the clinical findings.
For a successful treatment, one should know the findings of a radiograph precisely, it is then when a trained oral and maxillofacial radiologist comes into the picture. Especially for interpreting the radiographs taken with advanced imaging techniques.
This is the reason why oral and maxillofacial reporting is gaining importance globally.
About us and this blog
We are a Dental Teleradiology service provider offering online interpretation and reporting of dental radiology studies like OPG, Cone Beam CT (CBCT), Dental X Ray, Sialography etc.
Request a free quote
Please let us know about your reporting requirements so that we can send you our service proposal customized to your needs.
Subscribe to our newsletter!
More from our blog
See all postsRecent Posts
- Importance of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology in Dentistry July 1, 2021
- Dental 3D Scanning – A New Age Revolution June 30, 2021
- Looking After Your Oral Health in Festival Season June 16, 2021