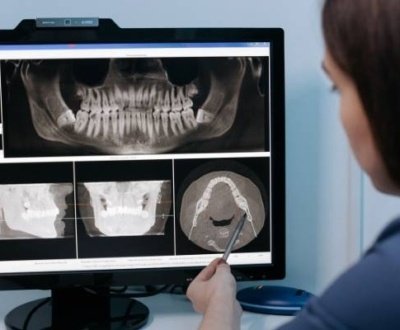
Digital radiography plays a vital role in today’s dental practice. It all started in 1987 when the pioneer of this field, also known as RadioVisioGraphy, was launched in the parts of Europe. Dr Francis Mouyen, the inventor of this technique, employed fibre optics for narrowing down a big X-ray image into a smaller size image that is further sensed by a charge-coupled device (CCD) image sensor chip.
But even after 25 years of its invention, digital radiography is not universally present in dental practices for various reasons including the problems that will be encountered during its use. The only difference between the digital radiography and conventional radiography is the type of image films. In digital radiography two types of image receptors are available: CCD and storage phosphor systems (SPS). These receptors are quite sensitive to the radiations thus much lower dose is required to generate image.
There are three different methods to evaluate these images:
- Direct method (uses electronic sensor)
- Indirect method (uses X-ray film scanner)
- Semi-indirect method (uses both electronic sensor and scanner)
Types and uses of digital dental radiographs:
Radiographs are of two types:
- Intraoral X-ray
- Extraoral X-ray
Intraoral X-ray:
It is the most common used X-ray technique. Features and uses of Intraoral X-ray include:
- Provide great detail
- Used to detect cavities
- Check the status of developing teeth
- Monitor teeth and bone health
Extraoral X-ray:
They are used to:
- Detect impacted teeth,
- Monitor jaw growth and development, and
- Identify potential problems between teeth, jaws and temporomandibular joints (TMJ), or other facial bones.
Decreased radiation dose:
Digital radiography is useful as it uses up to 50% lower radiation dose. It also conforms to the ALARA principle. One of the chief merits of this technique is that the image can be viewed in a variety of ways using image enhancement software and can be changed as per the needs.
Tools used to view the X-ray image are:
- Image processing (optimization of contrast and brightness of an image)
- Black/ white reversal (reversing the X-ray image so that radiolucent structures appear radiopaque and vice versa)
- Zoom (Magnification of the image)
- Digital subtraction radiography (Detect small differences between subsequent radiographs)
- Edge enhancement (converts contrast gradients into a texture that is visible as a shape)
Other advantages of Digital Radiography:
- Time saving
- Eliminates the need for the darkroom and chemical processing
- Teleradiography (transfer of a digital image to a distant site)
- Implant placement
Disadvantages of digital radiography:
- Initial cost of setting up the device is high.
- Higher cost of training the staff.
- Sensors can cause pharyngeal reflex and discomfort to the patients.
- Sensors need to be covered with disposable plastic sleeves as it cannot withstand heat.
In short, digital radiography provides a good alternative to the conventional radiography. The diagnostic quality of the newer technologies is higher along with lower radiation exposure to the patient. Newer software such as artificial intelligence is being developed in order to read the digital X-ray image. These changes are further destined to eliminate conventional radiography completely. Tags
About us and this blog
We are a Dental Teleradiology service provider offering online interpretation and reporting of dental radiology studies like OPG, Cone Beam CT (CBCT), Dental X Ray, Sialography etc.
Request a free quote
Please let us know about your reporting requirements so that we can send you our service proposal customized to your needs.
Subscribe to our newsletter!
More from our blog
See all postsRecent Posts
- Importance of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology in Dentistry July 1, 2021
- Dental 3D Scanning – A New Age Revolution June 30, 2021
- Looking After Your Oral Health in Festival Season June 16, 2021